Difference between revisions of "October 25, 2009"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Red Arrowhead= | =Red Arrowhead= | ||
| − | |||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg/97486824/LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg|LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg/97486824/LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg|LPOD-Oct25-09.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | ||
| − | <em>image by [mailto:revans_01420@yahoo.com Rick Evans]</em><br /> | + | <em>image by [mailto:revans_01420@yahoo.com" rel="nofollow Rick Evans]</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | I created this image of [http://www.lpod.org/archive/archive/2004/03/LPOD-2004-03-02.htm Mons Hansteen], a lunar [http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-iarticle_query?1975LPICo.234..189W&amp;data_type=PDF_HIGH&amp;whole_paper=YES&amp;type=PRINTER&amp;filetype=.pdf red spot], by performing principal component image analysis (PCA) on the five Clementine UVVIS multispectral band images (i.e. 415, 750, 900, 950 and 1000 nm). PCA is a tool sometimes used in multispectral geology [http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect5/Sect5_3.html studies] to reveal variations in mineral composition. Using <em>Photoshop</em> the Clementine images were loaded respectively into five alpha channels of a color image with the R, G and B channels deleted. With all alpha channels selected, [http://reindeergraphics.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=24&Itemid=47 FoveaPro 4.0] software was used to create a PCA transform and then to transform the alpha channel images into their respective principal component images. The first three resulting PCA images were then loaded respectively into the R, G and B channels of a color image producing the final image shown above. Mons Hansteen and all other lunar red spot features show up with a very distinctive reddish hue in such images. Lunar red spots seem to absorb preferentially in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum compared to the visible; other lunar mafic features including the central peaks of Tycho are fascinating to observe with this technique as well. <br /> | + | I created this image of [http://www.lpod.org/archive/archive/2004/03/LPOD-2004-03-02.htm" rel="nofollow Mons Hansteen], a lunar [http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/cgi-bin/nph-iarticle_query?1975LPICo.234..189W&amp;data_type=PDF_HIGH&amp;whole_paper=YES&amp;type=PRINTER&amp;filetype=.pdf" rel="nofollow red spot], by performing principal component image analysis (PCA) on the five Clementine UVVIS multispectral band images (i.e. 415, 750, 900, 950 and 1000 nm). PCA is a tool sometimes used in multispectral geology [http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect5/Sect5_3.html" rel="nofollow studies] to reveal variations in mineral composition. Using <em>Photoshop</em> the Clementine images were loaded respectively into five alpha channels of a color image with the R, G and B channels deleted. With all alpha channels selected, [http://reindeergraphics.com/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=24&Itemid=47" rel="nofollow FoveaPro 4.0] software was used to create a PCA transform and then to transform the alpha channel images into their respective principal component images. The first three resulting PCA images were then loaded respectively into the R, G and B channels of a color image producing the final image shown above. Mons Hansteen and all other lunar red spot features show up with a very distinctive reddish hue in such images. Lunar red spots seem to absorb preferentially in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum compared to the visible; other lunar mafic features including the central peaks of Tycho are fascinating to observe with this technique as well. <br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <em>[mailto:revans_01420@yahoo.com Rick Evans]</em><br /> | + | <em>[mailto:revans_01420@yahoo.com" rel="nofollow Rick Evans]</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <strong>Lunar History Note:</strong> Today is the 184th birthday of <em>perhaps</em> the greatest selenographer of the 19th century -[http://lpod.wikispaces.com/September+14,+2009 J.F. Julius Schmidt] (1825-1884). Thanks to [http://todayinastronomy.blogspot.com/2009/02/february-7-johann-friedrich-julius.html Mark Tillotson] for the reminder!<br /> | + | <strong>Lunar History Note:</strong> Today is the 184th birthday of <em>perhaps</em> the greatest selenographer of the 19th century -[http://lpod.wikispaces.com/September+14,+2009 J.F. Julius Schmidt] (1825-1884). Thanks to [http://todayinastronomy.blogspot.com/2009/02/february-7-johann-friedrich-julius.html" rel="nofollow Mark Tillotson] for the reminder!<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
Revision as of 19:14, 4 January 2015
Red Arrowhead
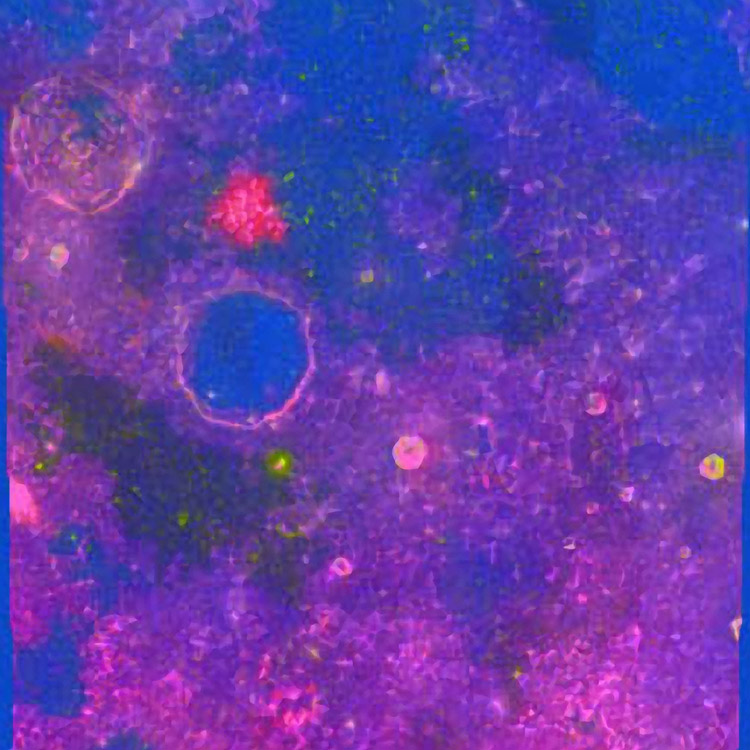
image by " rel="nofollow Rick Evans
I created this image of " rel="nofollow Mons Hansteen, a lunar " rel="nofollow red spot, by performing principal component image analysis (PCA) on the five Clementine UVVIS multispectral band images (i.e. 415, 750, 900, 950 and 1000 nm). PCA is a tool sometimes used in multispectral geology " rel="nofollow studies to reveal variations in mineral composition. Using Photoshop the Clementine images were loaded respectively into five alpha channels of a color image with the R, G and B channels deleted. With all alpha channels selected, " rel="nofollow FoveaPro 4.0 software was used to create a PCA transform and then to transform the alpha channel images into their respective principal component images. The first three resulting PCA images were then loaded respectively into the R, G and B channels of a color image producing the final image shown above. Mons Hansteen and all other lunar red spot features show up with a very distinctive reddish hue in such images. Lunar red spots seem to absorb preferentially in the ultraviolet region of the spectrum compared to the visible; other lunar mafic features including the central peaks of Tycho are fascinating to observe with this technique as well.
" rel="nofollow Rick Evans
Lunar History Note: Today is the 184th birthday of perhaps the greatest selenographer of the 19th century -J.F. Julius Schmidt (1825-1884). Thanks to " rel="nofollow Mark Tillotson for the reminder!
Related Links
Rükl plate 40



