Difference between revisions of "December 31, 2012"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=New Data And Personal Explorations= | =New Data And Personal Explorations= | ||
| + | <!-- Start of content --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg/395111840/LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg|LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg/395111840/LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg|LPOD-Dec31-12.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | ||
<em>images from LPODs over the last year</em><br /> | <em>images from LPODs over the last year</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
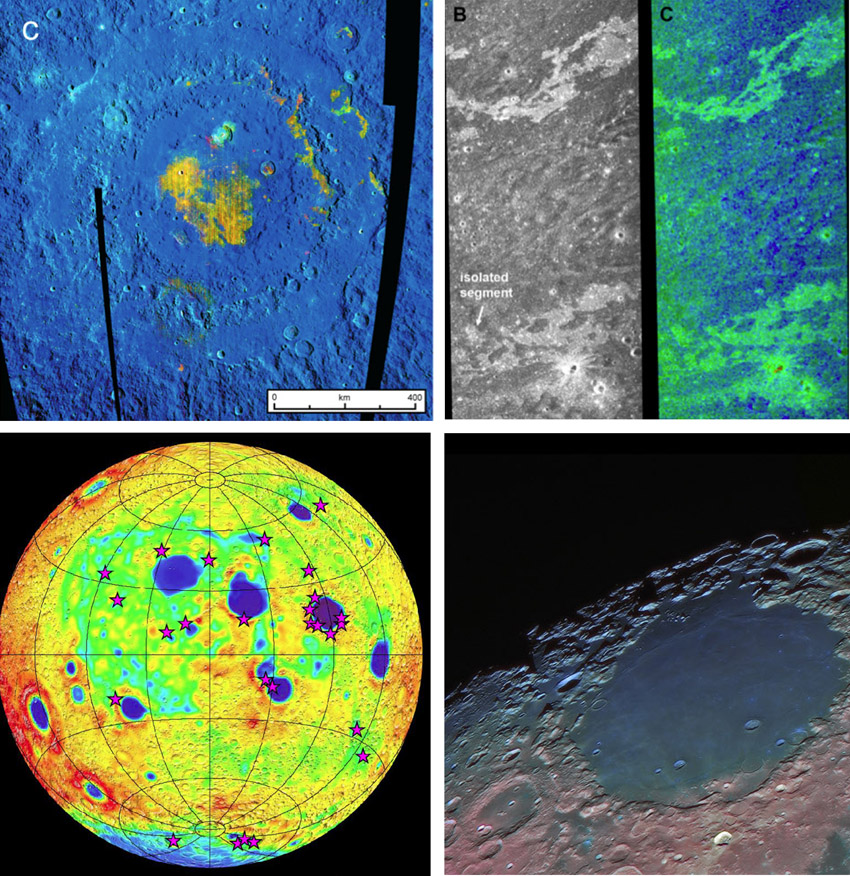
| − | Yesterday was [http://lpod. | + | Yesterday was [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/December_30,_2012 goodbyes] to inspiring lunar people, and today celebrates new data and understanding that appeared in 2012. The new data come from LRO that still orbits the Moon, and from other recent spacecraft such as Kaguya, Chandrayaan-1 and the recently departed GRAIL, all of whose data are still being mined. At upper left is a Moon Mineralogy Mapper [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/February_2,_2012 map] from Chandrayaan-1 that provides the highest quality compositional information ever for the Moon, in this case news about the sparse lavas within the Orientale Basin. The image at upper right displays impact melt flows mapped by the [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/March_3,_2012 Mini-RF] radar on Chandrayaan and LRO that were not previously so easily detected. Mini-RF also determined the distribution of ice in polar craters. GRAIL scientists created high precision crustal thickness [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/December_6,_2012 maps] (bottom left) by combining their spacecrafts' gravity data with altimetry from LRO. The purple stars are detections of olivine by the Kaguya spacecraft. The Crisium [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/October_19,_2012 view] represents the continuing tradition of innovative telescopic imaging by amateurs who combine techniques, and sometimes data from spacecraft, to make sure the Moon remains a place for personal explorations. <br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | ||
(And of course, un-illustrated here are the millions of high and hyper-resolution images from LRO that are the foundations for many lunar studies)<br /> | (And of course, un-illustrated here are the millions of high and hyper-resolution images from LRO that are the foundations for many lunar studies)<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[December 30, 2012|Lost Inspirations]] </p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[January 1, 2013|Comments?]] </p> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | + | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 08:26, 28 October 2018
New Data And Personal Explorations
images from LPODs over the last year
Yesterday was goodbyes to inspiring lunar people, and today celebrates new data and understanding that appeared in 2012. The new data come from LRO that still orbits the Moon, and from other recent spacecraft such as Kaguya, Chandrayaan-1 and the recently departed GRAIL, all of whose data are still being mined. At upper left is a Moon Mineralogy Mapper map from Chandrayaan-1 that provides the highest quality compositional information ever for the Moon, in this case news about the sparse lavas within the Orientale Basin. The image at upper right displays impact melt flows mapped by the Mini-RF radar on Chandrayaan and LRO that were not previously so easily detected. Mini-RF also determined the distribution of ice in polar craters. GRAIL scientists created high precision crustal thickness maps (bottom left) by combining their spacecrafts' gravity data with altimetry from LRO. The purple stars are detections of olivine by the Kaguya spacecraft. The Crisium view represents the continuing tradition of innovative telescopic imaging by amateurs who combine techniques, and sometimes data from spacecraft, to make sure the Moon remains a place for personal explorations.
Chuck Wood
(And of course, un-illustrated here are the millions of high and hyper-resolution images from LRO that are the foundations for many lunar studies)
Yesterday's LPOD: Lost Inspirations
Tomorrow's LPOD: Comments?
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



