image by Howard Eskildsen
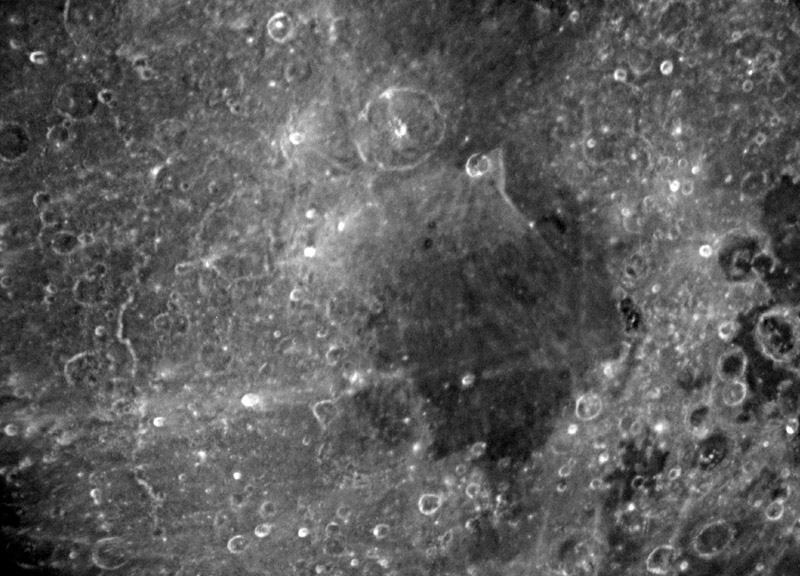
Here is a lunar surface caught in the act of changing its nature. Do you recognize Mare Nectaris and its surroundings at full Moon? When we see the mare under lower lighting the surface is dark and splotched only with a few small craters. But as the sun rises the darkness lightens and we can see rays from Tycho, Theophilus and other less easily traced sources. The effect of the rays is to veneer the mare darkness – due to dark minerals such as iron and magnesium – and gradually, ray by ray, convert it to a light-hued smooth terrain. If this process continues long enough it produces smooth light plains such as those near Hyginus and the Schiller-Zucchius basin. In some cases, small impact craters dig through the veneer and make dark halos – as seen here in Nectaris – confirming that old mare lavas lurk below. Here in Nectaris we have a delicate version of what we saw on the ejecta-penetrating radar image of the area near Crüger.
Technical Details:
Feb 10, 2006. Jose Olivarez’s 10″ f/15 refractor + 5X TeleXtender + MaxView 40 + Nikon Coolpix 4300.
Related Links:
Rükl charts 47 & 58
A wider view
Yesterday's LPOD: Mare Layering
Tomorrow's LPOD: Twin Peaks
COMMENTS?
Register, and click on the Discussion tab at the top of the page.
Contributions to http://www2.lpod.org/ are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution No-Derivative-Works Non-Commercial 3.0 License. 



