Difference between revisions of "June 18, 2013"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Maurice Collins recently pointed out to me a spectacular apparent oblique impact crater inside Daguerre on the north shore of Mare Nectaris. It turns out that | Maurice Collins recently pointed out to me a spectacular apparent oblique impact crater inside Daguerre on the north shore of Mare Nectaris. It turns out that | ||
this small crater has been noticed for a long time. It was beautifully seen on an Apollo 16 [http://www.hq.nasa.gov/office/pao/History/SP-362/ch5.2.htm image] back in the early 1970s, where it was interpreted as an | this small crater has been noticed for a long time. It was beautifully seen on an Apollo 16 [http://www.hq.nasa.gov/office/pao/History/SP-362/ch5.2.htm image] back in the early 1970s, where it was interpreted as an | ||
| − | oblique impact. I repeated that assessment in [ | + | oblique impact. I repeated that assessment in [[November 28, 2009|2009]] using a wonderful Kuguya image. In 2010, a LRO-NAC image led lunar scientist Irene Antonenko to a new |
[http://blog.moonzoo.org/2010/12/29/another-look-into-daguerre-crater-with-lroc/ interpetation]: the dark <em>zone of avoidance</em> is actually covered with dark ejecta rather than bright - it isn't an oblique impact crater at all. The LRO image shows | [http://blog.moonzoo.org/2010/12/29/another-look-into-daguerre-crater-with-lroc/ interpetation]: the dark <em>zone of avoidance</em> is actually covered with dark ejecta rather than bright - it isn't an oblique impact crater at all. The LRO image shows | ||
that dark material crops out just below the crater rim crest. It could be pyroclastic material from the volcanic vents along Daguerre's north rim. Or it could be | that dark material crops out just below the crater rim crest. It could be pyroclastic material from the volcanic vents along Daguerre's north rim. Or it could be | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
outcrops of dark material to the right of the dark ejecta but that seems less continuous than the rim exposure that caused the ejecta and the cascading dark | outcrops of dark material to the right of the dark ejecta but that seems less continuous than the rim exposure that caused the ejecta and the cascading dark | ||
material toward the crater floor. If you explore the dark ejecta on the NAC [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc_browse/view/M121993376R image] you will see that the dark material mantles pre-existing craters, softening | material toward the crater floor. If you explore the dark ejecta on the NAC [http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc_browse/view/M121993376R image] you will see that the dark material mantles pre-existing craters, softening | ||
| − | their morphology and being draped over everything. Irene points out that my old friend [ | + | their morphology and being draped over everything. Irene points out that my old friend [[April 7, 2012|Farouk El Baz]] speculated back in Apollo days that the darkness could |
be due to <em>an abrupt lateral change in the composition of the bedrock within the area that was excavated.</em> As usual, Farouk was right, as was Irene, and also | be due to <em>an abrupt lateral change in the composition of the bedrock within the area that was excavated.</em> As usual, Farouk was right, as was Irene, and also | ||
James Ashley who wrote in 2012 an LRO Featured Image [http://www.lroc.asu.edu/news/index.php?/archives/636-Diversity.html#extended article] on this fake oblique impact crater. Makes you wonder how many other presumed obliques | James Ashley who wrote in 2012 an LRO Featured Image [http://www.lroc.asu.edu/news/index.php?/archives/636-Diversity.html#extended article] on this fake oblique impact crater. Makes you wonder how many other presumed obliques | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_47 47]<br /> | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_47 47]<br /> | ||
| − | <em>[ | + | <em>[[21st Century Atlas of the Moon|21st Century Atlas]]</em> chart 6.<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[June 17, 2013|A Proto-Patrick Moore]] </p> | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[June 17, 2013|A Proto-Patrick Moore]] </p> | ||
Latest revision as of 09:07, 28 October 2018
It's a Fake!
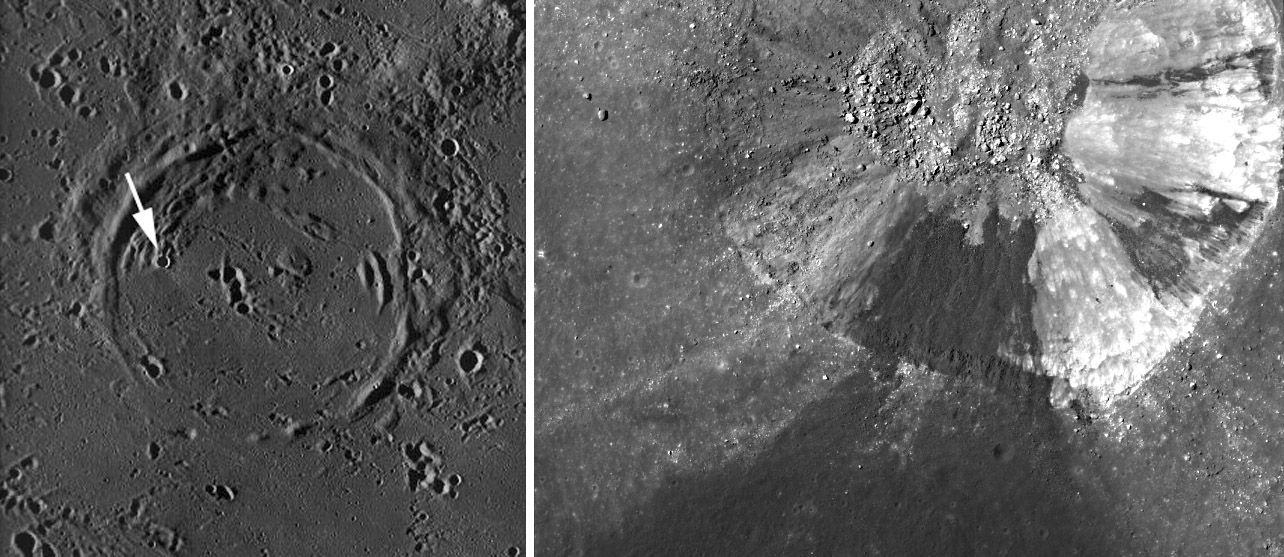
LRO images from Moon-WIki (John Moore) and NAC (NASA/ASU)
Maurice Collins recently pointed out to me a spectacular apparent oblique impact crater inside Daguerre on the north shore of Mare Nectaris. It turns out that
this small crater has been noticed for a long time. It was beautifully seen on an Apollo 16 image back in the early 1970s, where it was interpreted as an
oblique impact. I repeated that assessment in 2009 using a wonderful Kuguya image. In 2010, a LRO-NAC image led lunar scientist Irene Antonenko to a new
interpetation: the dark zone of avoidance is actually covered with dark ejecta rather than bright - it isn't an oblique impact crater at all. The LRO image shows
that dark material crops out just below the crater rim crest. It could be pyroclastic material from the volcanic vents along Daguerre's north rim. Or it could be
pulverized mare lava. Because it is not the topmost layer on the little crater it probably is not impact melt from the small crater's formation. In any case it may
have a limited occurrence under the crater, explaining why the dark ejecta is localized to the southern quarter of the ejecta field. Actually there are some
outcrops of dark material to the right of the dark ejecta but that seems less continuous than the rim exposure that caused the ejecta and the cascading dark
material toward the crater floor. If you explore the dark ejecta on the NAC image you will see that the dark material mantles pre-existing craters, softening
their morphology and being draped over everything. Irene points out that my old friend Farouk El Baz speculated back in Apollo days that the darkness could
be due to an abrupt lateral change in the composition of the bedrock within the area that was excavated. As usual, Farouk was right, as was Irene, and also
James Ashley who wrote in 2012 an LRO Featured Image article on this fake oblique impact crater. Makes you wonder how many other presumed obliques
might be target inhomogeneities.
Chuck Wood
Related Links
Rükl plate 47
21st Century Atlas chart 6.
Yesterday's LPOD: A Proto-Patrick Moore
Tomorrow's LPOD: Still Fighting Old Wars
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



