Difference between revisions of "October 19, 2004"
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
===COMMENTS?=== | ===COMMENTS?=== | ||
Register, and click on the <b>Discussion</b> tab at the top of the page. | Register, and click on the <b>Discussion</b> tab at the top of the page. | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | You can support LPOD when you buy any book from Amazon thru [[Support_ LPOD|LPOD]]! | ||
| + | --> | ||
| + | <span style="font-size:88%"> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | Contributions to http://www2.lpod.org/ are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution No-Derivative-Works Non-Commercial 3.0 License. [http://www.creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0 http://www.wikispaces.com/i/creativecommons/by-nc-nd_3.0_80x15.png]<br> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </span> | ||
Revision as of 11:21, 1 February 2015
Rays of Light
Image Credit: Robert Spellman |
|
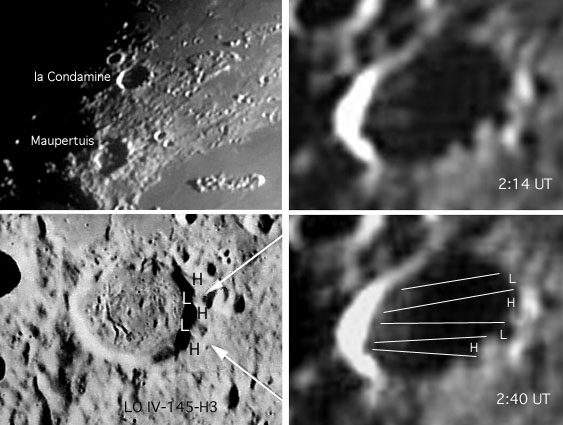
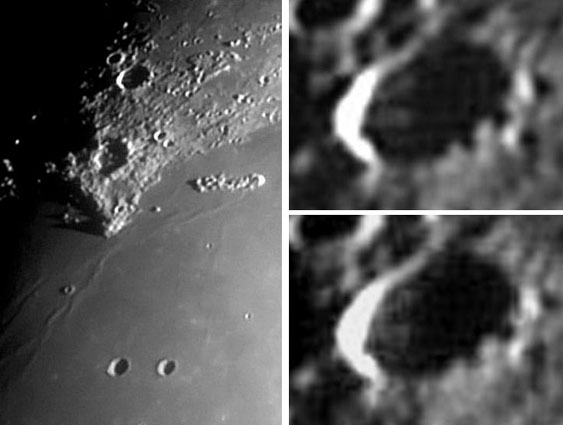
Rays of Light As the sun rises over a crater, its rim casts a long shadow across the floor. If the rim were of even height and the floor were perfectly flat, the shadow would be a smooth curve. This is what most small simple craters look like (the BIO types). But larger craters have more topographic variations in their rims and floors. Long sunrise (or sunset) shadows map out local high spots in the rim, and bright bands or rays between shadows mark where the peaks are lower. And the neat thing is that these bright and dark rays are fun to observe, partially because they are only visible for a few hours each month. Here Robert Spellman has captured shadows and bright cones streaking the floor of the crater la Condamine in the rubble behind Sinus Iridum. By use of a video camera, he documented variations in the bright and darks bands through time. The upper left image was taken at 2:14 UT and the bottom right one was 26 minutes later. You can see that the shadows shortened slightly. On the mouseover image I have drawn lines that bound the bright and dark bands and show how they connect back to locally high (H) and low (L) spots on the crater rim. On Robert's web site he also shows the Lunar Orbiter IV image that I have annotated to match his photos. The Orbiter image shows that the rim of la Condamine is mostly even except for where it has been cut by secondary craters. The image also shows that la Condamine is a floor-fractured crater with an uneven floor. So here, I would guess, shadows and bright bands are mostly due to rim height variations, with some complexity added by floor roughness. Technical Details: Related Links: Tomorrow's LPOD: Rough Domes |
|
Author & Editor: Technical Consultant: Contact Translator: A service of: |
COMMENTS?
Register, and click on the Discussion tab at the top of the page.
Contributions to http://www2.lpod.org/ are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution No-Derivative-Works Non-Commercial 3.0 License.