Difference between revisions of "March 21, 2010"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg/129087265/LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg|LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg/129087265/LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg|LPOD-Mar21-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | ||
| − | <em>image by [mailto:howardeskildsen@msn.com | + | <em>image by [mailto:howardeskildsen@msn.com Howard Eskildsen], Florida</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Most dark halo craters (DHC) on maria are normal impact craters that penetrated bright crater rays or ejecta and excavated underlying dark basaltic lavas. Howard has begun an investigation to see if DHC can be used to determine thicknesses of crater rays. He marked (with short turquoise lines) all the DHC he could find in the area east of Copernicus. He notes that the greatest concentrations of DHC are where the rays appear the thinnest (because the mare surface is not very bright), which areas he has marked with circles. Outside of the circles there are fewer DHC and they have larger diameters, presumably since it takes a larger impact to penetrate the deeper ray layers closer to Copernicus. One of the largest DHC in the area is the 4.6 km wide Copernicus H. Accepting that the transient cavity formed early in an impact was about 30% of the crater's diameter, suggests that the bright ray and ejecta material where H formed is about 1.4 km deep. That is much thicker than a ray is likely to be, but H formed close enough to Copernicus to be on top of the thick continuous ejecta deposit. Howard finds that for the smaller DHC further from Copernicus (in the circles) the implied ray thicknesses are more like 100 m. Because rays themselves do not cast shadows they are presumably much thinner than 100 m, but Howard's method is a good approach to mapping variations in ray thickness. Using higher resolution and high Sun Clementine images would allow detection of smaller DHC permitting more accurate ray thickness determinations - a good project.<br /> | Most dark halo craters (DHC) on maria are normal impact craters that penetrated bright crater rays or ejecta and excavated underlying dark basaltic lavas. Howard has begun an investigation to see if DHC can be used to determine thicknesses of crater rays. He marked (with short turquoise lines) all the DHC he could find in the area east of Copernicus. He notes that the greatest concentrations of DHC are where the rays appear the thinnest (because the mare surface is not very bright), which areas he has marked with circles. Outside of the circles there are fewer DHC and they have larger diameters, presumably since it takes a larger impact to penetrate the deeper ray layers closer to Copernicus. One of the largest DHC in the area is the 4.6 km wide Copernicus H. Accepting that the transient cavity formed early in an impact was about 30% of the crater's diameter, suggests that the bright ray and ejecta material where H formed is about 1.4 km deep. That is much thicker than a ray is likely to be, but H formed close enough to Copernicus to be on top of the thick continuous ejecta deposit. Howard finds that for the smaller DHC further from Copernicus (in the circles) the implied ray thicknesses are more like 100 m. Because rays themselves do not cast shadows they are presumably much thinner than 100 m, but Howard's method is a good approach to mapping variations in ray thickness. Using higher resolution and high Sun Clementine images would allow detection of smaller DHC permitting more accurate ray thickness determinations - a good project.<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com | + | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | <div>You can support LPOD when you buy any book from Amazon thru [http://www.lpod.org/?page_id=591 | + | <div>You can support LPOD when you buy any book from Amazon thru [http://www.lpod.org/?page_id=591 LPOD!]<br /> |
</div> | </div> | ||
---- | ---- | ||
===COMMENTS?=== | ===COMMENTS?=== | ||
| − | + | Register, and click on the <b>Discussion</b> tab at the top of the page. | |
Revision as of 16:17, 11 January 2015
How Thick Are Rays?
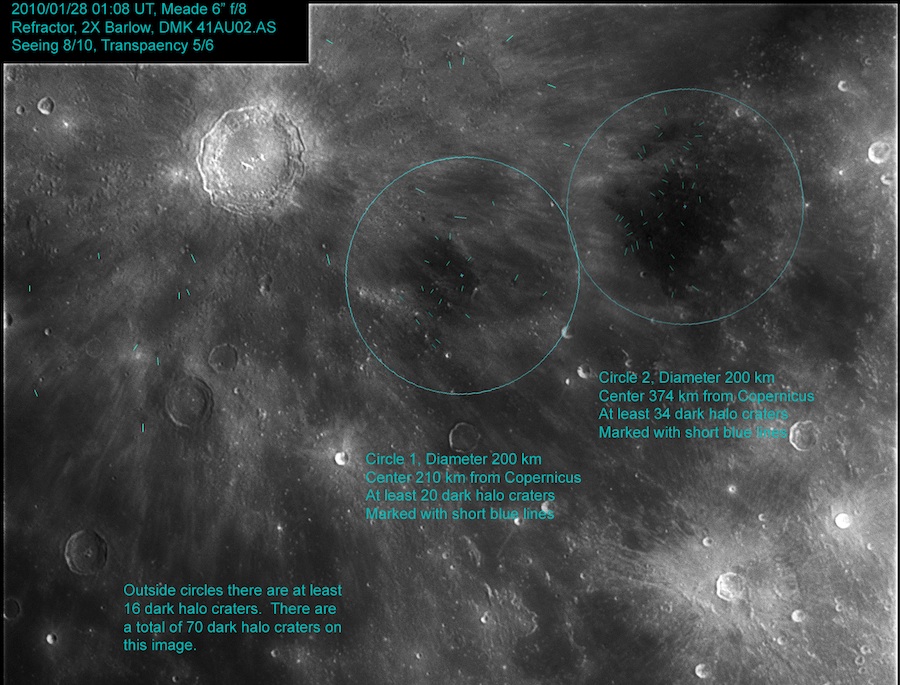
image by Howard Eskildsen, Florida
Most dark halo craters (DHC) on maria are normal impact craters that penetrated bright crater rays or ejecta and excavated underlying dark basaltic lavas. Howard has begun an investigation to see if DHC can be used to determine thicknesses of crater rays. He marked (with short turquoise lines) all the DHC he could find in the area east of Copernicus. He notes that the greatest concentrations of DHC are where the rays appear the thinnest (because the mare surface is not very bright), which areas he has marked with circles. Outside of the circles there are fewer DHC and they have larger diameters, presumably since it takes a larger impact to penetrate the deeper ray layers closer to Copernicus. One of the largest DHC in the area is the 4.6 km wide Copernicus H. Accepting that the transient cavity formed early in an impact was about 30% of the crater's diameter, suggests that the bright ray and ejecta material where H formed is about 1.4 km deep. That is much thicker than a ray is likely to be, but H formed close enough to Copernicus to be on top of the thick continuous ejecta deposit. Howard finds that for the smaller DHC further from Copernicus (in the circles) the implied ray thicknesses are more like 100 m. Because rays themselves do not cast shadows they are presumably much thinner than 100 m, but Howard's method is a good approach to mapping variations in ray thickness. Using higher resolution and high Sun Clementine images would allow detection of smaller DHC permitting more accurate ray thickness determinations - a good project.
Chuck Wood
Related Links
Rükl plate 31
COMMENTS?
Register, and click on the Discussion tab at the top of the page.



