Difference between revisions of "May 1, 2004"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Serenitatis Diameter Sequence= | =Serenitatis Diameter Sequence= | ||
| − | + | <p> | |
| − | + | <table width="640" border="0" align="center" cellpadding="6" cellspacing="2"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | </table> | |
| − | + | <table width="640" border="0" align="center" cellpadding="6" cellspacing="2"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td><div align="center">[[File:LPOD-2004-05-01.jpeg|LPOD-2004-05-01.jpeg]]</div></td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td><div align="center"> | |
| − | + | <p class="main_sm">Image Credit: [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/research/lunar_orbiter/" class="one Lunar & Planetary Lab Consolidated Lunar Atlas]</p> | |
| − | + | </div></td> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | </table> | |
| − | + | <table class="story" border="0" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" width="90%" cellpadding="10" align="center"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td><p class="Story" align="center"><b>Serenitatis Diameter Sequence</b></p> | |
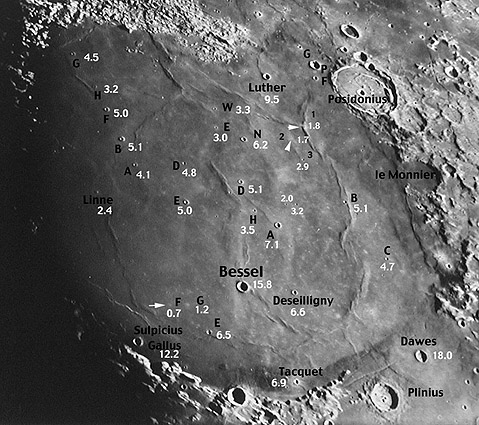
| − | + | <p class="Story" align="left">Have you heard of the North Polar Sequence? It is a series of 96 stars near Polaris whose brightnesses and colors were accurately determined as standards for stellar astronomers. There has not been a comparable standard sequence that would permit lunar observers to judge their observing conditions, telescopic performance, visual acuity or imaging limits. The above image of Mare Serenitatis (and the mouseover larger version) is the first attempt to provide such a standard sequence of crater diameters for lunar astronomers. Serenitatis is a good place for a lunar diameter sequence because it is a relatively uncomplicated surface with a small number of pristine craters that can be confidently identified with a little care. An important characteristic of a standard sequence is its accuracy. I have measured all of these crater diameters, some during the early 1970s when I led a project to catalog lunar craters using Lunar Orbiter IV images. I made other measures in the last few days, using the 1:1,000,000 Mare Serenitatis Lunar Map published by NASA in 1976, and online [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/research/lunar_orbiter/ Lunar Orbiter images]. Most of the diameters are probably correct within 100-200 m. This Consolidated Lunar Atlas image, obtained with a 61" reflector, seems to have a resolution of about 2 km - craters larger have clearly defined rims, and smaller ones show up only as small white spots. Today, amateur imagers with telescopes 1/10th this aperture can equal and exceed this wonderful CLA image. </p> | |
| − | + | <blockquote> | |
| − | + | <p align="right" class="Story">— [mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</p> | |
| − | + | </blockquote> <p class="story" align="left"><b>Technical Details</b>:<br>I have used the classic nomenclature, rather than the needless new names that replace lettered designations. The equivalences are: Bessel E = Bobillier; Linne E = Banting; Bessel A = Sarabhai; Le Monnier B = Very; Le Monnier C = Borel. Remember, the letter is placed on the side of its crater closest to it patronymic crater - e.g. the A for Bessel A is on a line between Bessel A and Bessel. Note that I have given diameters for a few craters west of Posidonius that lack designations - to reduce future ambiguity I number them 1 thru 3. | |
| − | + | <p class="story" align="left"><B>Related Links:</B><br> | |
| − | + | [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/research/lunar_orbiter/bin/info.shtml?209 Lunar Orbiter IV View 1]<br> | |
| − | + | [http://www.lpi.usra.edu/research/lunar_orbiter/bin/info.shtml?251 Lunar Orbiter IV View 2] | |
| − | + | <p class="story"><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> Lunar Eclipse Preview</p> | |
| − | + | </tr> | |
| − | + | </table> | |
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | + | <p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>Author & Editor:</b><br> | |
| − | + | [mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Charles A. Wood]</p> | |
| − | + | <p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>Technical Consultant:</b><br> | |
| − | + | [mailto:anthony@perseus.gr Anthony Ayiomamitis]</p> | |
| − | + | <p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>A service of:</b><br> | |
| − | + | [http://www.observingthesky.org/ ObservingTheSky.Org]</p> | |
| − | + | <p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>Visit these other PODs:</b> <br> | |
| − | + | [http://antwrp.gsfc.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html Astronomy] | [http://www.msss.com/ Mars] | [http://epod.usra.edu/ Earth]</p> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<p> </p> | <p> </p> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
===COMMENTS?=== | ===COMMENTS?=== | ||
Click on this icon [[image:PostIcon.jpg]] at the upper right to post a comment. | Click on this icon [[image:PostIcon.jpg]] at the upper right to post a comment. | ||
Revision as of 17:19, 4 January 2015
Serenitatis Diameter Sequence
Serenitatis Diameter Sequence Have you heard of the North Polar Sequence? It is a series of 96 stars near Polaris whose brightnesses and colors were accurately determined as standards for stellar astronomers. There has not been a comparable standard sequence that would permit lunar observers to judge their observing conditions, telescopic performance, visual acuity or imaging limits. The above image of Mare Serenitatis (and the mouseover larger version) is the first attempt to provide such a standard sequence of crater diameters for lunar astronomers. Serenitatis is a good place for a lunar diameter sequence because it is a relatively uncomplicated surface with a small number of pristine craters that can be confidently identified with a little care. An important characteristic of a standard sequence is its accuracy. I have measured all of these crater diameters, some during the early 1970s when I led a project to catalog lunar craters using Lunar Orbiter IV images. I made other measures in the last few days, using the 1:1,000,000 Mare Serenitatis Lunar Map published by NASA in 1976, and online Lunar Orbiter images. Most of the diameters are probably correct within 100-200 m. This Consolidated Lunar Atlas image, obtained with a 61" reflector, seems to have a resolution of about 2 km - craters larger have clearly defined rims, and smaller ones show up only as small white spots. Today, amateur imagers with telescopes 1/10th this aperture can equal and exceed this wonderful CLA image. Technical Details: Related Links: Tomorrow's LPOD: Lunar Eclipse Preview |
Author & Editor:
Charles A. Wood
Technical Consultant:
Anthony Ayiomamitis
A service of:
ObservingTheSky.Org
Visit these other PODs:
Astronomy | Mars | Earth
COMMENTS?
Click on this icon File:PostIcon.jpg at the upper right to post a comment.