Difference between revisions of "May 12, 2012"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=Copernicus Almost From Lunar Orbit= | =Copernicus Almost From Lunar Orbit= | ||
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="http://lpod.wikispaces.com/file/view/LPOD-May12-12.jpg/333876102/LPOD-May12-12.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-May12-12.jpg|LPOD-May12-12.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | |
<em>image by [mailto:mwirths@starband.ne Michael Wirths], Baja California, Mexico</em><br /> | <em>image by [mailto:mwirths@starband.ne Michael Wirths], Baja California, Mexico</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 23:29, 2 January 2015
Copernicus Almost From Lunar Orbit
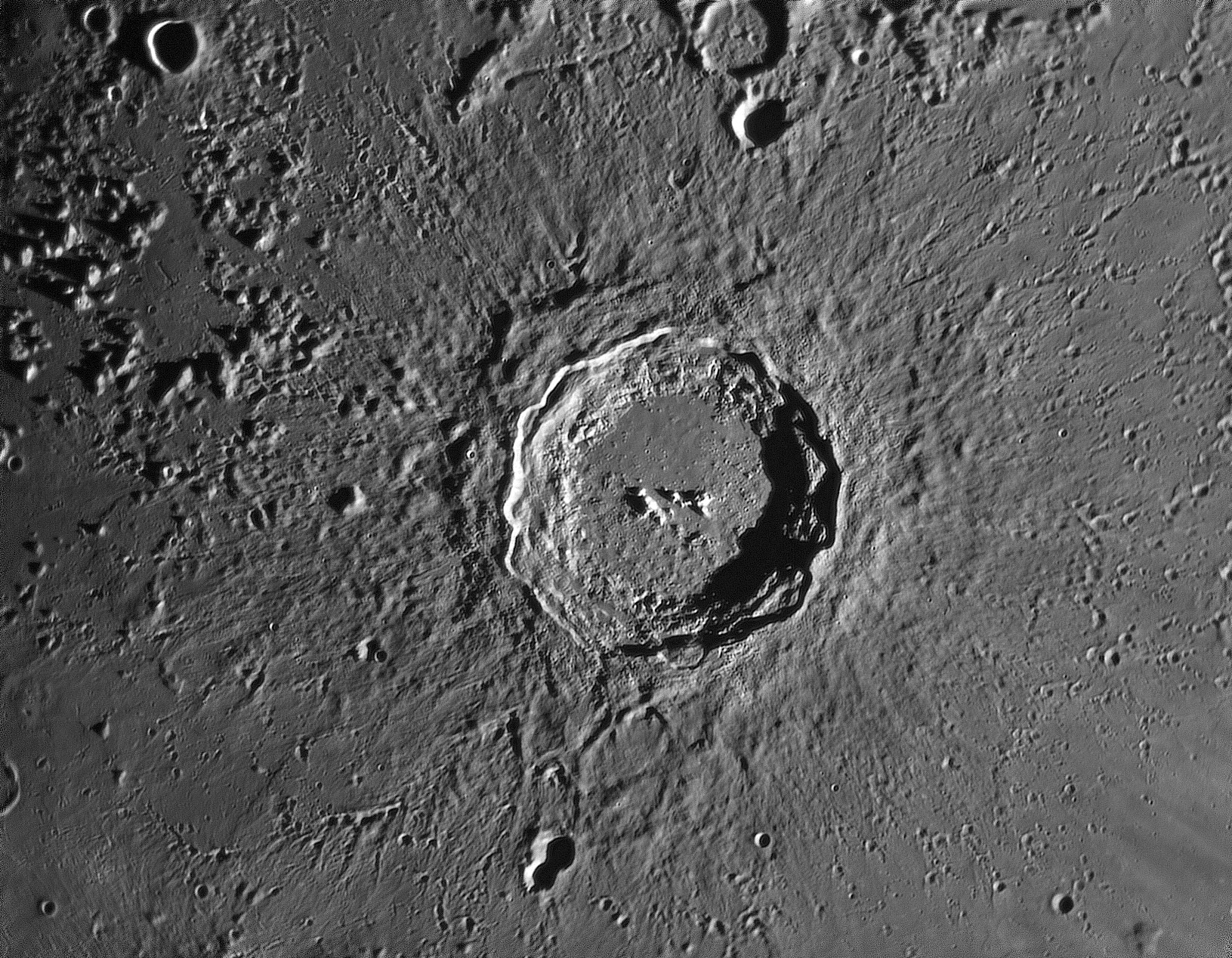
image by Michael Wirths, Baja California, Mexico
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter camera team has been issuing a series of high resolution images that document
the varieties of impact melt morphologies. That is very important but Mike with his Baja spaceship is demonstrating
that you don't need an orbiter to acquire magnificent images of melt deposits. Most impressive are the tongues
of melt outside the arc of Copernicus' rim from Fauth (twin craters at bottom) to the mountain at the 9 o'clock
position. Just south of the mountain is a superb tongue of melt that built up levees on its flanks as it flowed. Once
this classic example of a melt flow is recognized it is easier to see others on the arc toward Fauth. Melt ponds are
also visible at various places inside the rim on terrace tops. And the smooth northwest quadrant of Copernicus' floor
is veneered by impact melt. Along the southern edge of the image secondary craters and their characteristic herring-
bone pattern of wrap around ejecta are beautifully seen, while the ridge and furrow continuous ejecta is well seen
along the top of the image. If we had been able to take images like this in the 1950s scientists might have decided
that they didn't need to go to the Moon.
Chuck Wood
Technical Details
2012/04/30 at 20:47 PST; taken with 18" Starmaster dob (Zambuto optics) a Lumenera Infinity 2-2 camera, 2.5X Televue Powermate barlow and R/IR filter.
Processed with AviStack and PS CS.
Related Links
Rükl plate 31



