Difference between revisions of "June 9, 2010"
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ =Selenometrics= <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-June9-10.jpg/1477888...") |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Selenometrics= | =Selenometrics= | ||
| − | + | <!-- Start of content --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-June9-10.jpg/147788801/LPOD-June9-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-June9-10.jpg|LPOD-June9-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | |
<em>image by [mailto:howardeskildsen@msn.com Howard Eskildsen], Florida</em><br /> | <em>image by [mailto:howardeskildsen@msn.com Howard Eskildsen], Florida</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | With LRO, Kaguya and other recent lunar orbiters it might be thought that amateurs have nothing to contribute to understanding the Moon. The wording of that sentence hints that I don't agree. One example is topography. As previous [mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | + | With LRO, Kaguya and other recent lunar orbiters it might be thought that amateurs have nothing to contribute to understanding the Moon. The wording of that sentence hints that I don't agree. One example is topography. As previous [http://www.lpod.org/index.php?s=diameters&paged=3 LPODs] have documented there are considerable differences in reported values of depths and even diameters of craters. Such information is fundamental to characterizing the morphology of the Moon. The high resolution altimetry from the orbiters will greatly improve many types of lunar investigations but it is not certain that it will result in improved catalogs of crater dimensions. I say this because software created to automatically identify craters by the circles of their rims is still laughably inaccurate. But software tools can greatly increase the efficiency of humans, who are unexcelled at recognizing craters, in measuring their depths and diameters. The [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/May_12,_2010 Moon Zoo] does exactly that for crater diameters, and Howard is using Jim Mosher's increasingly valuable [https://the-moon.us/wiki/LTVT LTVT] software to measure elevations for Pitatus. Howard's values are consistent with Dick Pike's determination of a crater depth of 680 m, and are probably an improvement of the estimated central peak heigh of 1000 m from Sekiguchi whose measures were pioneering but often crude. How do I know these previous values - just looked them up at the [https://the-moon.us/wiki/Pitatus Moon Wiki], of course! Howard's experiments were done on images from a small telescope; using the same techniques with high resolution amateur images can result in new information where none is available. Or maybe Jim or someone else will write software that will allow amateurs to rapidly determine crater diameters and depths from the LRO digital terrain date.<br /> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Rükl plate [ | + | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_54 54]<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | + | <table class="wiki_table"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td> <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> | |
| − | ---- | + | <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> |
| − | + | </td> | |
| − | + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[June 8, 2010|A Radially Expanding Atmosphere?]] </p> | |
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[June 10, 2010|Bellissimo]] </p> | ||
| + | <!-- End of content --> | ||
| + | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:31, 28 October 2018
Selenometrics
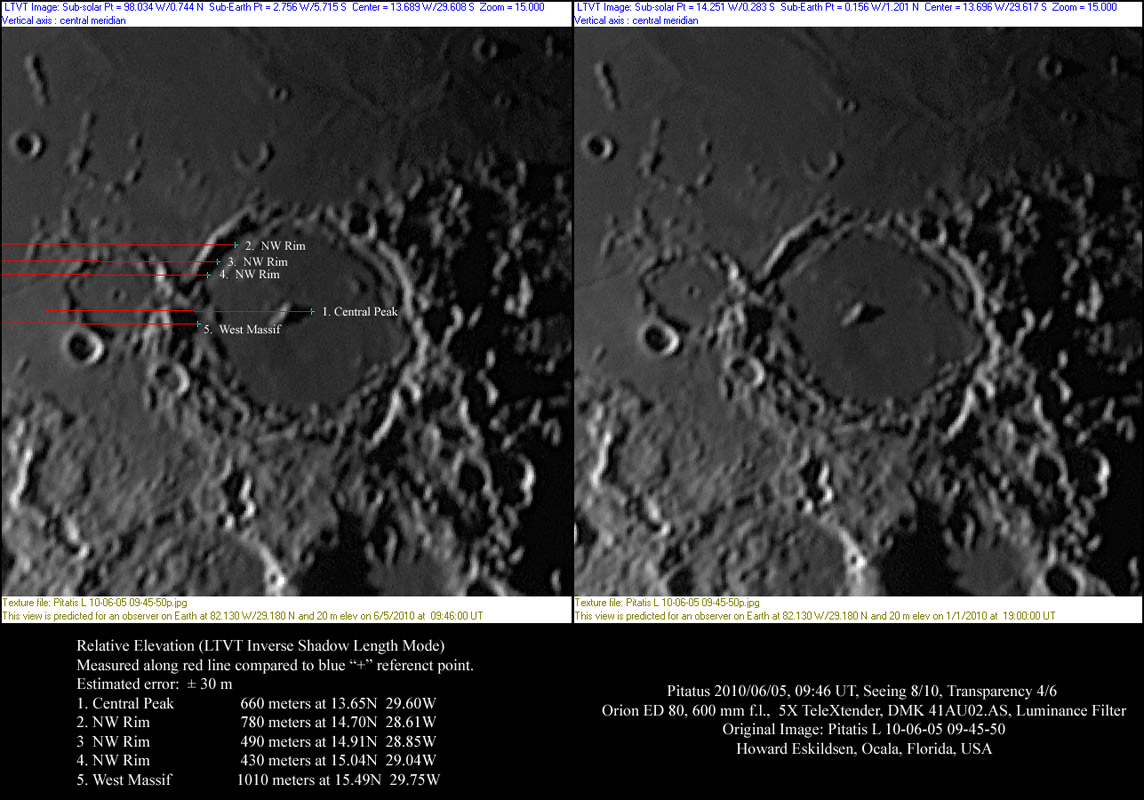
image by Howard Eskildsen, Florida
With LRO, Kaguya and other recent lunar orbiters it might be thought that amateurs have nothing to contribute to understanding the Moon. The wording of that sentence hints that I don't agree. One example is topography. As previous LPODs have documented there are considerable differences in reported values of depths and even diameters of craters. Such information is fundamental to characterizing the morphology of the Moon. The high resolution altimetry from the orbiters will greatly improve many types of lunar investigations but it is not certain that it will result in improved catalogs of crater dimensions. I say this because software created to automatically identify craters by the circles of their rims is still laughably inaccurate. But software tools can greatly increase the efficiency of humans, who are unexcelled at recognizing craters, in measuring their depths and diameters. The Moon Zoo does exactly that for crater diameters, and Howard is using Jim Mosher's increasingly valuable LTVT software to measure elevations for Pitatus. Howard's values are consistent with Dick Pike's determination of a crater depth of 680 m, and are probably an improvement of the estimated central peak heigh of 1000 m from Sekiguchi whose measures were pioneering but often crude. How do I know these previous values - just looked them up at the Moon Wiki, of course! Howard's experiments were done on images from a small telescope; using the same techniques with high resolution amateur images can result in new information where none is available. Or maybe Jim or someone else will write software that will allow amateurs to rapidly determine crater diameters and depths from the LRO digital terrain date.
Chuck Wood
Related Links
Rükl plate 54
Yesterday's LPOD: A Radially Expanding Atmosphere?
Tomorrow's LPOD: Bellissimo
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



