Difference between revisions of "October 30, 2008"
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ =Rotated Mountains?= <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:7:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg/4424565...") |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Rotated Mountains?= | =Rotated Mountains?= | ||
| + | <!-- Start of content --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:7:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg/44245659/LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg|LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:7 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:7:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg/44245659/LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg|LPOD-Oct30-08.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:7 --><br /> | ||
<em>image by [mailto:g.tarsoudis@freemail.gr George Tarsoudis], Greece</em><br /> | <em>image by [mailto:g.tarsoudis@freemail.gr George Tarsoudis], Greece</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | Most of the Moon's [ | + | Most of the Moon's [https://the-moon.us/wiki/Lunar_Mons 18 mountain ranges] (<em>montes</em> in IAU's Latin) are related to impact basins, typically being part of a basin rim or ring. The Caucaus Mountains, captured here on a slant, are undoubtedly related to a basin, presumably Imbrium to the west, but the oblique angle of the Caucasus makes makes the relation unclear. The fact that the Caucasus are highest on their western edge, with a bright scarp front like the Apennines, suggest that they are part of Imbrium's rim. But if you draw a [http://www.lpod.org/coppermine/displayimage.php?pid=2326&fullsize=1 circle] around Imbrium to mark its rim, the Caucasus deviate from the circle; have they somehow been rotated counterclockwise a few degrees? Actually the southern end of the Caucasus - as far north as the area of Theaetetus - lies near the rim circle, but the Caucasus bend toward the east there and are progressively further east of the circle to the north. I have noticed before that Cassini is a break in the Imbrium-circling mountains and have [[March_19,_2006|speculated]] that the area behind (east of it) has been filled in with lava after the Caucasus rotated eastward. Sounds like a good story. <br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Rükl plate [ | + | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/Rükl_13 13]<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[October 29, 2008|A Sharper Image]] </p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[October 31, 2008|Sub-Polar Marker]] </p> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | |||
{{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:56, 13 October 2018
Rotated Mountains?
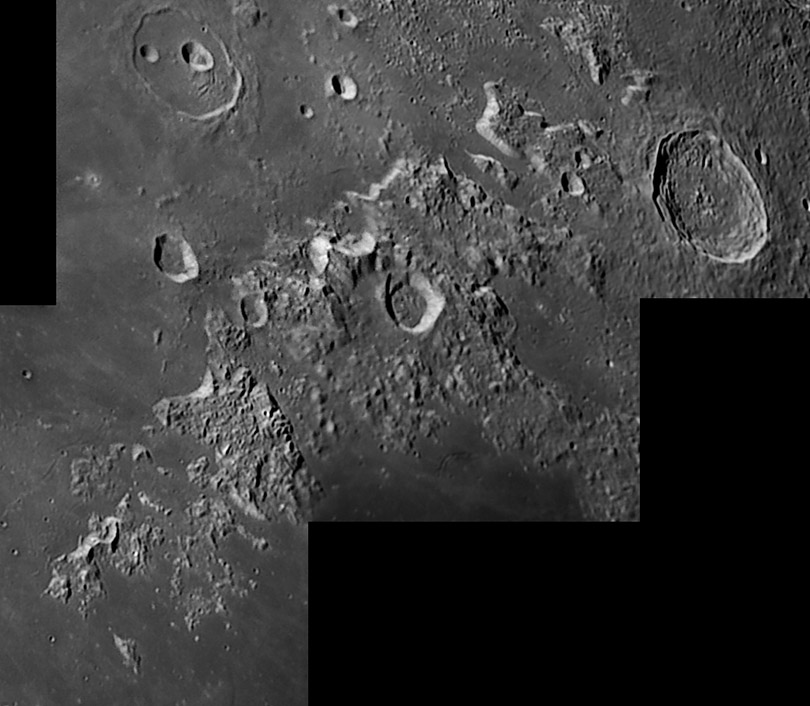
image by George Tarsoudis, Greece
Most of the Moon's 18 mountain ranges (montes in IAU's Latin) are related to impact basins, typically being part of a basin rim or ring. The Caucaus Mountains, captured here on a slant, are undoubtedly related to a basin, presumably Imbrium to the west, but the oblique angle of the Caucasus makes makes the relation unclear. The fact that the Caucasus are highest on their western edge, with a bright scarp front like the Apennines, suggest that they are part of Imbrium's rim. But if you draw a circle around Imbrium to mark its rim, the Caucasus deviate from the circle; have they somehow been rotated counterclockwise a few degrees? Actually the southern end of the Caucasus - as far north as the area of Theaetetus - lies near the rim circle, but the Caucasus bend toward the east there and are progressively further east of the circle to the north. I have noticed before that Cassini is a break in the Imbrium-circling mountains and have speculated that the area behind (east of it) has been filled in with lava after the Caucasus rotated eastward. Sounds like a good story.
Chuck Wood
Technical Details
22 July 2008. Newtonian 10 inch st f/6.3 + DMK21AF04 + barlow 3X + Red filter with IR-cut; mosaic 7 images, Image processing Registax 4.0 and PS CS3.
Related Links
Rükl plate 13
Yesterday's LPOD: A Sharper Image
Tomorrow's LPOD: Sub-Polar Marker
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



