Difference between revisions of "February 5, 2010"
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ =Seeing in the Dark= <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Feb5-10.jpg/118...") |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Seeing in the Dark= | =Seeing in the Dark= | ||
| − | + | <!-- Start of content --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Feb5-10.jpg/118225987/LPOD-Feb5-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Feb5-10.jpg|LPOD-Feb5-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | |
<em>images by [mailto:paolo@lazzarotti-optics.com Paolo Lazzarotti], Massa, Italy</em><br /> | <em>images by [mailto:paolo@lazzarotti-optics.com Paolo Lazzarotti], Massa, Italy</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
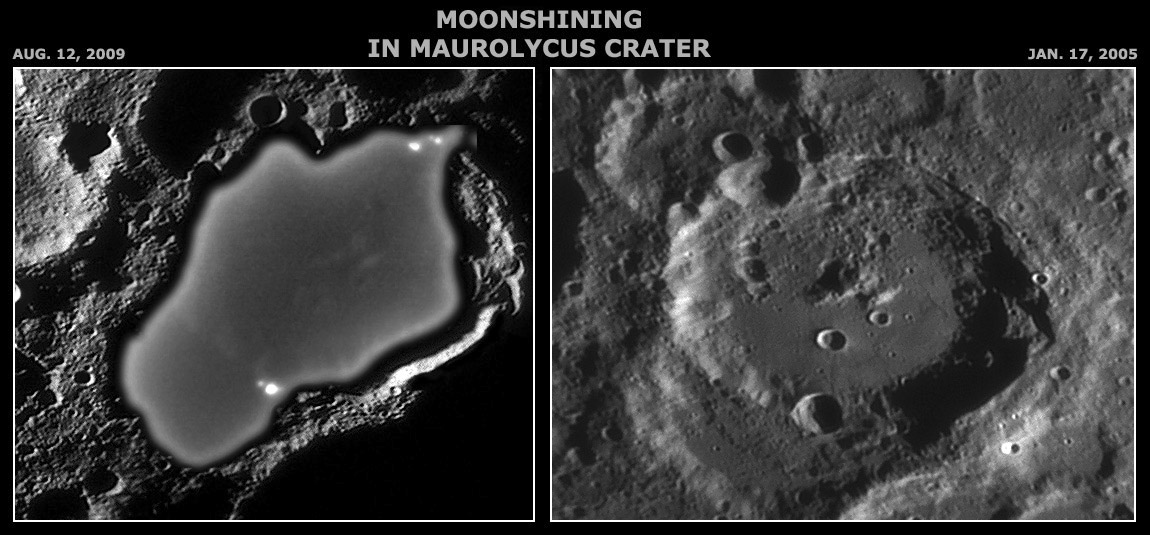
| − | Under a very dark sky, I have heard, you can see by the starlight. And certainly the full Moon makes enough illumination to take midnight hikes. Somewhere between those extremes are the shadowed areas within lunar craters. The shadows are inky black, without an atmosphere to scatter light, but are the shadowed areas completely black? The answer is doubly no. We know that the very sensitive camera on the Kaguya orbiter could image the always shadowed [http://lpod. | + | Under a very dark sky, I have heard, you can see by the starlight. And certainly the full Moon makes enough illumination to take midnight hikes. Somewhere between those extremes are the shadowed areas within lunar craters. The shadows are inky black, without an atmosphere to scatter light, but are the shadowed areas completely black? The answer is doubly no. We know that the very sensitive camera on the Kaguya orbiter could image the always shadowed [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/October_24,_2008 floor] of Shackleton. And now we see that some Earthly cameras can also penetrate lunar shadows. Paolo manipulated one of his normal high quality [http://www.lazzarotti-hires.com/wp/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/stofler-heraclitus-licetus20090812_0207_lazz.jpg images] of the Maurolycus area, greatly spreading the dark part of the image over a wide range of pixel values. This revealed faint bright spots on the floor of the crater. Comparison with an earlier image he had taken of Maurolycus (right) demonstrates that Paolo imaged the central peaks and craters on the floor of Maurolycus. Presumably light bounced off the illuminated right wall of Maurolycus provided the faint light that reflected off the floor details.</span> I am not aware if this has been accomplished before from Earth, but it will undoubtedly lead many observers to hyper-enhance their images, perhaps looking to investigate what degree of wall illumination best reveals enshadowed details. This discovery will not provide new details of lunar topography, for what we see faintly will become clear as the Sun rises over a crater. But it does suggest two other things. First, when the Chinese reach the Moon they may be able to work in shadowed areas near the terminator, using military style light enhancement goggles. Second, permanently shadowed polar craters are constantly bathed in very feeble light reflected from the upper parts of their illuminated rims. It may be that over a billion years, this is enough light and heat to sublime ice deposits. Perhaps that is why there was surprisingly [http://www2.lpod.org/wiki/November_14,_2009 little water] released by the LCROSS impact in Cabaeus.<br /> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Technical Details</strong><br /> | <strong>Technical Details</strong><br /> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Rükl plate [ | + | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_66 66]<br /> |
Paolo's [http://www.lazzarotti-hires.com/ website]<br /> | Paolo's [http://www.lazzarotti-hires.com/ website]<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[February 4, 2010|Fold a Moon]] </p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[February 6, 2010|Not the Center of Attention]] </p> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | + | <table class="wiki_table"> | |
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td> <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> | |
| − | ---- | + | <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> |
| − | + | </td> | |
| − | + | <!-- End of content --> | |
| + | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 07:27, 28 October 2018
Seeing in the Dark
images by Paolo Lazzarotti, Massa, Italy
Under a very dark sky, I have heard, you can see by the starlight. And certainly the full Moon makes enough illumination to take midnight hikes. Somewhere between those extremes are the shadowed areas within lunar craters. The shadows are inky black, without an atmosphere to scatter light, but are the shadowed areas completely black? The answer is doubly no. We know that the very sensitive camera on the Kaguya orbiter could image the always shadowed floor of Shackleton. And now we see that some Earthly cameras can also penetrate lunar shadows. Paolo manipulated one of his normal high quality images of the Maurolycus area, greatly spreading the dark part of the image over a wide range of pixel values. This revealed faint bright spots on the floor of the crater. Comparison with an earlier image he had taken of Maurolycus (right) demonstrates that Paolo imaged the central peaks and craters on the floor of Maurolycus. Presumably light bounced off the illuminated right wall of Maurolycus provided the faint light that reflected off the floor details. I am not aware if this has been accomplished before from Earth, but it will undoubtedly lead many observers to hyper-enhance their images, perhaps looking to investigate what degree of wall illumination best reveals enshadowed details. This discovery will not provide new details of lunar topography, for what we see faintly will become clear as the Sun rises over a crater. But it does suggest two other things. First, when the Chinese reach the Moon they may be able to work in shadowed areas near the terminator, using military style light enhancement goggles. Second, permanently shadowed polar craters are constantly bathed in very feeble light reflected from the upper parts of their illuminated rims. It may be that over a billion years, this is enough light and heat to sublime ice deposits. Perhaps that is why there was surprisingly little water released by the LCROSS impact in Cabaeus.
Chuck Wood
Technical Details
Left image: Aug. 12, 2009, 02:07 UT. Gladius CF-315 Lazzarotti Opt. telescope + LV-11392 PRO experimental camera + Edmund Optics R filter, 100 of 2000 frames stacked; right one: Jan. 17, 2005
Related Links
Rükl plate 66
Paolo's website
Yesterday's LPOD: Fold a Moon
Tomorrow's LPOD: Not the Center of Attention
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



