Difference between revisions of "April 18, 2013"
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=A Prinzly Origin= | =A Prinzly Origin= | ||
| − | + | <!-- Start of content --> | |
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:0:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg/424139614/LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg|LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg/424139614/LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg|LPOD-Apr18-13.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:6 --><br /> | ||
<em>image from [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/store/10.1029/2011JE004000/asset/jgre3033.pdf?v=1&t=hfnbp4ap&s=71b798d67f2569602c5e37f8613ead8972fce9fa Hurwitz and colleagues (2012)]</em><br /> | <em>image from [http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/store/10.1029/2011JE004000/asset/jgre3033.pdf?v=1&t=hfnbp4ap&s=71b798d67f2569602c5e37f8613ead8972fce9fa Hurwitz and colleagues (2012)]</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | It has been known since the late 60s and early 70s that lunar sinuous rilles are volcanic lava channels or tubes. Over time improved | + | It has been known since the late 60s and early 70s that lunar sinuous rilles are volcanic lava channels or tubes. Over time improved mathematical models of the physical processes that create sinuous rilles, and improved measurements of their dimensions, have led to more and |
| − | + | more refinements of the details of the eruptions. The latest comes from Debra Hurwitz, Jim Head, Lionel Wilson and Harry Hiesinger in a paper | |
| − | more refinements of the details of the eruptions. The latest comes from Debra Hurwitz, Jim Head, Lionel Wilson and Harry Hiesinger in a paper | + | that is freely available online. Their model suggest that the Prinz Rille shown here formed by thermal erosion as a new flow of lava melted into |
| − | that is freely available online. Their model suggest that the Prinz Rille shown here formed by thermal erosion as a new flow of lava melted into | + | pre-existing lavas. Mechanical erosion - the new flow digging into the early one - is less effective on the Moon than Earth because of lower |
| − | pre-existing lavas. Mechanical erosion - the new flow digging into the early one - is less effective on the Moon than Earth because of lower | + | gravity and very gentle slopes. It turns out that the chemical composition also significantly affects the efficiency of thermal erosion through |
| − | gravity and very gentle slopes. It turns out that the chemical composition also significantly affects the efficiency of thermal erosion through | + | the temperature likely to be associated with different compositions. The hotter the new lava the more effectively it can melt the underlying |
| − | the temperature likely to be associated with different compositions. The hotter the new lava the more effectively it can melt the underlying | + | lava, of course. The hottest lavas known in Earth history were [http://www3.imperial.ac.uk/earthscienceandengineering/aboutese/hottopic/pasttopics/komatiites komatiites] that also had very low viscosity - they flowed easily - which |
| − | lava, of course. The hottest lavas known in Earth history were [http://www3.imperial.ac.uk/earthscienceandengineering/aboutese/hottopic/pasttopics/komatiites komatiites] that also had very low viscosity - they flowed easily - which | + | increases thermal erosion. No komatiities have been found on the Moon so models with that composition give a upper limit for how rapidly the |
| − | increases thermal erosion. No komatiities have been found on the Moon so models with that composition give a upper limit for how rapidly the | + | Prinz Rilles was formed - about 0.4 years. If the magmas were low-titanium mare basalts the rille may have been active for 2.2 years. One |
| − | Prinz Rilles was formed - about 0.4 years. If the magmas were low-titanium mare basalts the rille may have been active for 2.2 years. One | + | thing that LPOD previously [[February_19,_2007|noted]] is that nearly all sinuous rilles occur in the Procellarum KREEP Terrain which has the highest measured |
| − | thing that LPOD previously [ | + | radioactivity on the Moon. Perhaps the likely high magma temperatures associated with PKT magmas led to the common occurences of |
| − | radioactivity on the Moon. Perhaps the likely high magma temperatures associated with PKT magmas led to the common occurences of | + | sinuous rilles. |
| − | sinuous rilles.<br /> | + | <br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Rükl plate [ | + | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_19 19]<br /> |
| − | <em>[ | + | <em>[[21st Century Atlas of the Moon|21st Century Atlas]]</em> chart 21.<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[April 17, 2013|A Submerged Terrain]] </p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[April 19, 2013|Unseen]] </p> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| + | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | ||
Latest revision as of 08:22, 28 October 2018
A Prinzly Origin
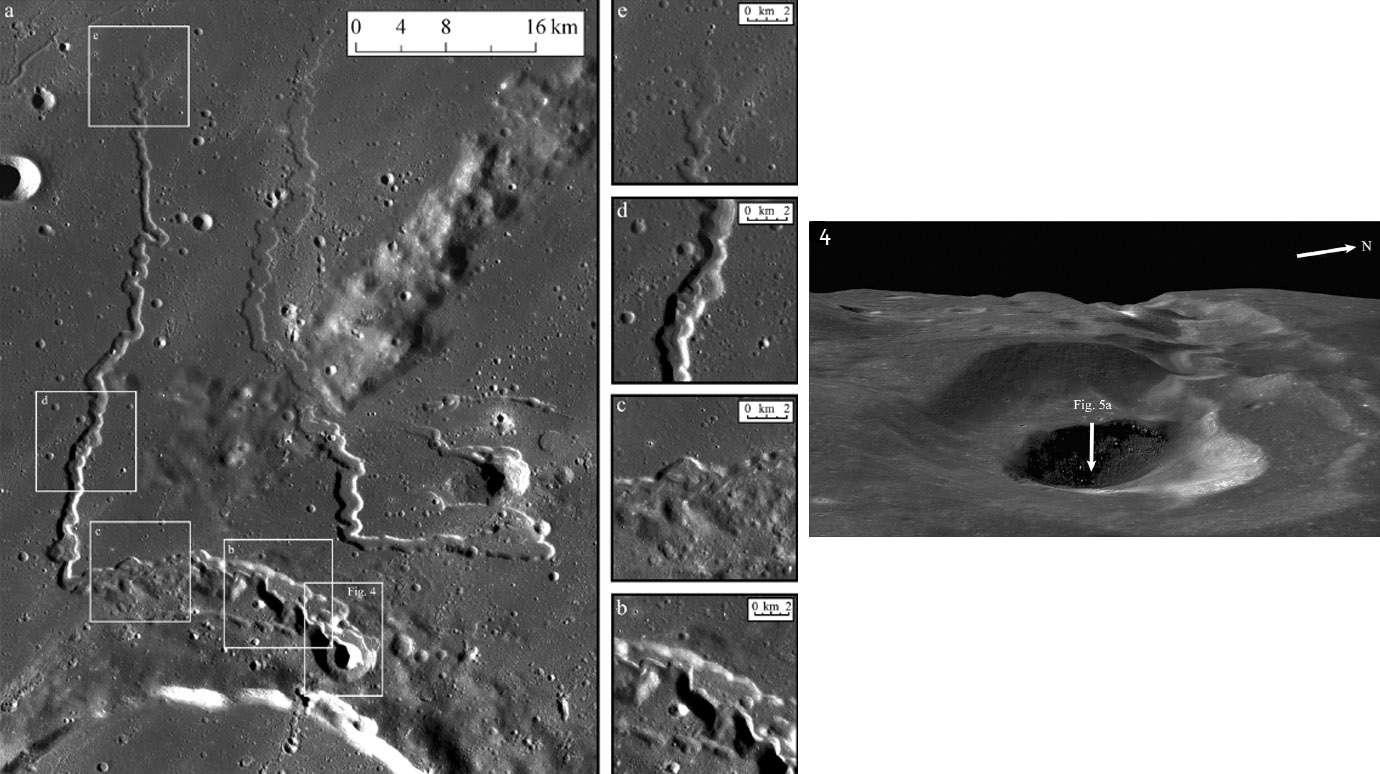
image from Hurwitz and colleagues (2012)
It has been known since the late 60s and early 70s that lunar sinuous rilles are volcanic lava channels or tubes. Over time improved mathematical models of the physical processes that create sinuous rilles, and improved measurements of their dimensions, have led to more and
more refinements of the details of the eruptions. The latest comes from Debra Hurwitz, Jim Head, Lionel Wilson and Harry Hiesinger in a paper
that is freely available online. Their model suggest that the Prinz Rille shown here formed by thermal erosion as a new flow of lava melted into
pre-existing lavas. Mechanical erosion - the new flow digging into the early one - is less effective on the Moon than Earth because of lower
gravity and very gentle slopes. It turns out that the chemical composition also significantly affects the efficiency of thermal erosion through
the temperature likely to be associated with different compositions. The hotter the new lava the more effectively it can melt the underlying
lava, of course. The hottest lavas known in Earth history were komatiites that also had very low viscosity - they flowed easily - which
increases thermal erosion. No komatiities have been found on the Moon so models with that composition give a upper limit for how rapidly the
Prinz Rilles was formed - about 0.4 years. If the magmas were low-titanium mare basalts the rille may have been active for 2.2 years. One
thing that LPOD previously noted is that nearly all sinuous rilles occur in the Procellarum KREEP Terrain which has the highest measured
radioactivity on the Moon. Perhaps the likely high magma temperatures associated with PKT magmas led to the common occurences of
sinuous rilles.
Chuck Wood
Technical Details
A treasure trove of 35 normally restricted journal articles, including the one discussed today, of LRO results is available here.
Related Links
Rükl plate 19
21st Century Atlas chart 21.
Yesterday's LPOD: A Submerged Terrain
Tomorrow's LPOD: Unseen
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



