Difference between revisions of "March 13, 2010"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Rays, Rays Everywhere= | =Rays, Rays Everywhere= | ||
| − | + | <!-- Start of content --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | |
| − | + | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-Mar13-10.jpg/127260951/LPOD-Mar13-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-Mar13-10.jpg|LPOD-Mar13-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | |
<em>image by [mailto:webmaster@skytrip.de Mario Weigand]</em><br /> | <em>image by [mailto:webmaster@skytrip.de Mario Weigand]</em><br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Rükl plate [ | + | Rükl plate [https://the-moon.us/wiki/R%C3%BCkl_27 27]<br /> |
Mario's [http://www.SkyTrip.de webpage]<br /> | Mario's [http://www.SkyTrip.de webpage]<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| + | <p><b>Yesterday's LPOD:</b> [[March 12, 2010|Wiggly Lines]] </p> | ||
| + | <p><b>Tomorrow's LPOD:</b> [[March 14, 2010|Lunar Ice Discovered in 1904]] </p> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | |||
<table class="wiki_table"> | <table class="wiki_table"> | ||
| − | + | <tr> | |
| − | + | <td> <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> | |
| − | + | <!-- RemoveRevolverMaps --> | |
| − | + | </td> | |
| − | ---- | + | <!-- End of content --> |
| − | + | {{wiki/ArticleFooter}} | |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:51, 13 October 2018
Rays, Rays Everywhere
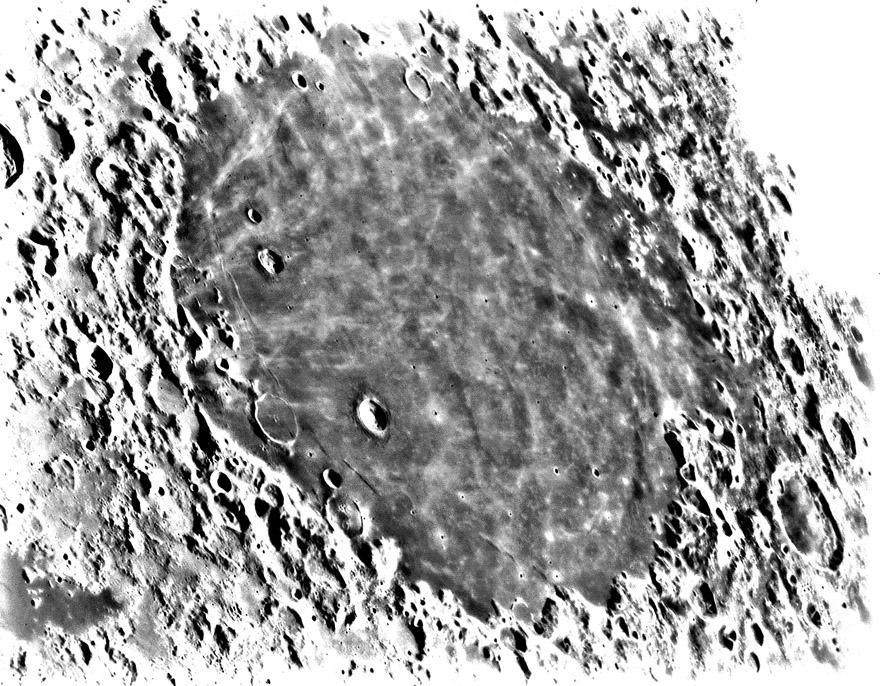
image by Mario Weigand
Observing near full Moon there is a clash of albedos, with bright rays from Copernicus, Aristarchus and other young craters winging across dark maria. But how dark are the maria, really? In this image - with sincere apologies to Mario! - I have severely enhanced the gray portion of the histogram to reveal that Mare Crisium is crossed by ray material nearly everywhere. Five radial swaths of rays in western Crisium radiate away from Proclus, but the sources for most of the other ray fragments can not be easily identified. Crisium and other maria are contaminated with faint filagrees of bright material, some being immature mare rocks - for example, the little nimbi surrounding fresh small craters in the mare - and other being anorthositic material from the highlands. This means that there can be small secondary craters virtually anywhere - complicating age dating by crater counting - and that mare samples collected by space probes - Luna 24 landed in the bottom right corner of Crisium - are contaminated by a patina of non-local material.
Chuck Wood
Technical Details
04/22/2007, 20:48 CEST (18:48 UT). Celestron C11 + DMK 21 BF04 FireWire-Camera
Mario's image appears in its natural state in the LPOD Photo Gallery.
Related Links
Rükl plate 27
Mario's webpage
Yesterday's LPOD: Wiggly Lines
Tomorrow's LPOD: Lunar Ice Discovered in 1904
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.



