Difference between revisions of "May 13, 2010"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
=Basinal Surprises= | =Basinal Surprises= | ||
| − | |||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextHeadingRule:1:<h1> --> | ||
<!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-May13-10.jpg/141620447/LPOD-May13-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-May13-10.jpg|LPOD-May13-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | <!-- ws:start:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16:<img src="/file/view/LPOD-May13-10.jpg/141620447/LPOD-May13-10.jpg" alt="" title="" /> -->[[File:LPOD-May13-10.jpg|LPOD-May13-10.jpg]]<!-- ws:end:WikiTextLocalImageRule:16 --><br /> | ||
| − | <em>crustal thickness (in km) map from [http://wms.selene.jaxa.jp/selene_viewer/jpn/observation_mission/rsat/rsat_007.html Kaguya Image Gallery]</em><br /> | + | <em>crustal thickness (in km) map from [http://wms.selene.jaxa.jp/selene_viewer/jpn/observation_mission/rsat/rsat_007.html" rel="nofollow Kaguya Image Gallery]</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | What causes holes in the ground? For the Moon, the only thing we know is impacts. Impact cratering digs a hole about one-third as deep as the crater is wide for small craters, with the ratio falling off to perhaps 1:10 or less as diameters increase. To dig deep holes requires big cratering events. This recent map of the lunar crustal thickness from Kaguya is the most accurate in existence. It reveals major crustal thinning for large basins - for example the Crisium Basin thinned the crust from about 70 km thickness to 5 km. These large anomalies were well known from earlier data, but much smaller crustal thinnings were harder to detect, often being lost in measurement uncertainty. Here are a couple of better resolved crustal anomalies that probably represent buried impact basins. Starting at upper left is a thinning of 10-15 km exactly centered on [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071202 Lamont]. The origin of this ring of mare ridges has long been controversial, but with this new data it appears that USGS mapper Dave Scott was correct, 36 years ago when he proposed it was a small impact basin covered by Tranquillitatis lavas. More surprising is the much stronger thinning anomaly centered west of [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071006 Sinus Asperitatis]. The existence of the West Asperitatis Basin explains the continuation of scattered high topography northwest of the curved rim of the Nectaris Basin. Like many other basins the WAB lacks a rim on one side - the east. Moving into Mare Fecunditatis is another surprising basin. This is surprising because although a basin is expected under each roughly circular patch of mare, this one, the Ibn Battuta-Lindbergh Basin, is smaller than expected. The contour lines don't seem to follow the mare ridges, suggesting a complicated story. Finally, at bottom right is a small anomaly that gives confidence in the others. The thinning is right in the middle of the previously hypothesized 500 km wide [http://the-moon.wikispaces.com/Balmer-Kapteyn Balmer-Kapteyn Basin]. As you explore the entire crustal thickness map the most unexpected thinning is for the Crüger Basin, which [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071006 LPOD] has already explored.<br /> | + | What causes holes in the ground? For the Moon, the only thing we know is impacts. Impact cratering digs a hole about one-third as deep as the crater is wide for small craters, with the ratio falling off to perhaps 1:10 or less as diameters increase. To dig deep holes requires big cratering events. This recent map of the lunar crustal thickness from Kaguya is the most accurate in existence. It reveals major crustal thinning for large basins - for example the Crisium Basin thinned the crust from about 70 km thickness to 5 km. These large anomalies were well known from earlier data, but much smaller crustal thinnings were harder to detect, often being lost in measurement uncertainty. Here are a couple of better resolved crustal anomalies that probably represent buried impact basins. Starting at upper left is a thinning of 10-15 km exactly centered on [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071202" rel="nofollow Lamont]. The origin of this ring of mare ridges has long been controversial, but with this new data it appears that USGS mapper Dave Scott was correct, 36 years ago when he proposed it was a small impact basin covered by Tranquillitatis lavas. More surprising is the much stronger thinning anomaly centered west of [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071006" rel="nofollow Sinus Asperitatis]. The existence of the West Asperitatis Basin explains the continuation of scattered high topography northwest of the curved rim of the Nectaris Basin. Like many other basins the WAB lacks a rim on one side - the east. Moving into Mare Fecunditatis is another surprising basin. This is surprising because although a basin is expected under each roughly circular patch of mare, this one, the Ibn Battuta-Lindbergh Basin, is smaller than expected. The contour lines don't seem to follow the mare ridges, suggesting a complicated story. Finally, at bottom right is a small anomaly that gives confidence in the others. The thinning is right in the middle of the previously hypothesized 500 km wide [http://the-moon.wikispaces.com/Balmer-Kapteyn Balmer-Kapteyn Basin]. As you explore the entire crustal thickness map the most unexpected thinning is for the Crüger Basin, which [http://www.lpod.org/?m=20071006" rel="nofollow LPOD] has already explored.<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Chuck Wood]</em><br /> | + | <em>[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com" rel="nofollow Chuck Wood]</em><br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | <strong>Related Links</strong><br /> | ||
| − | Yoshiaki Ishihara and others (2009) [http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2009/2009GL039708.shtml Crustal thickness of the Moon: Implications for farside basin structures]. <em>Geophysical Research Letters 36</em>, L19202, 4 PP., 2009. doi:10.1029/2009GL039708<br /> | + | Yoshiaki Ishihara and others (2009) [http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2009/2009GL039708.shtml" rel="nofollow Crustal thickness of the Moon: Implications for farside basin structures]. <em>Geophysical Research Letters 36</em>, L19202, 4 PP., 2009. doi:10.1029/2009GL039708<br /> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| − | <div>You can support LPOD when you buy any book from Amazon thru [http://www.lpod.org/?page_id=591 LPOD!]<br /> | + | <div>You can support LPOD when you buy any book from Amazon thru [http://www.lpod.org/?page_id=591" rel="nofollow LPOD!]<br /> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | |||
---- | ---- | ||
===COMMENTS?=== | ===COMMENTS?=== | ||
Click on this icon [[image:PostIcon.jpg]] at the upper right to post a comment. | Click on this icon [[image:PostIcon.jpg]] at the upper right to post a comment. | ||
Revision as of 18:22, 4 January 2015
Basinal Surprises
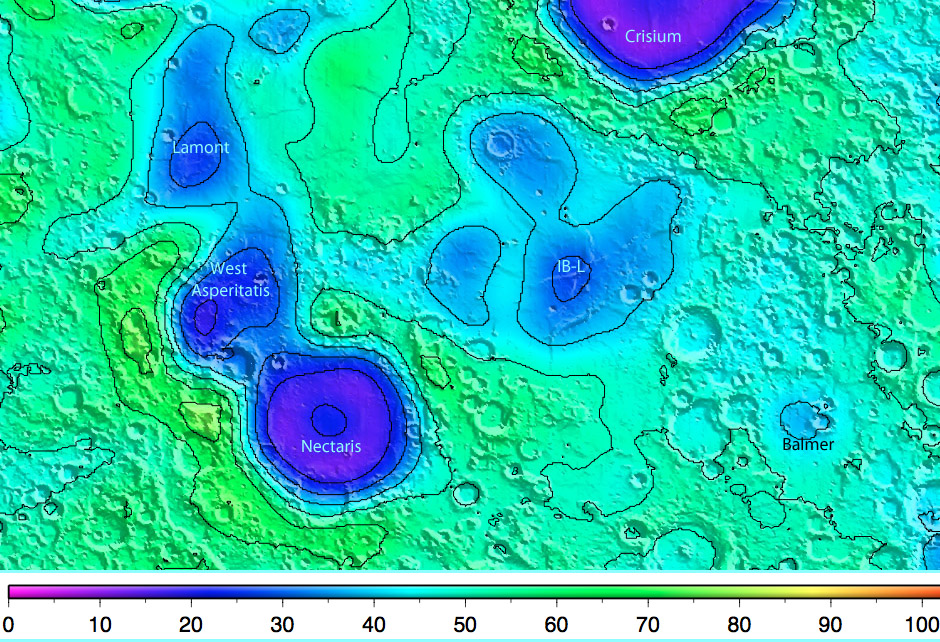
crustal thickness (in km) map from " rel="nofollow Kaguya Image Gallery
What causes holes in the ground? For the Moon, the only thing we know is impacts. Impact cratering digs a hole about one-third as deep as the crater is wide for small craters, with the ratio falling off to perhaps 1:10 or less as diameters increase. To dig deep holes requires big cratering events. This recent map of the lunar crustal thickness from Kaguya is the most accurate in existence. It reveals major crustal thinning for large basins - for example the Crisium Basin thinned the crust from about 70 km thickness to 5 km. These large anomalies were well known from earlier data, but much smaller crustal thinnings were harder to detect, often being lost in measurement uncertainty. Here are a couple of better resolved crustal anomalies that probably represent buried impact basins. Starting at upper left is a thinning of 10-15 km exactly centered on " rel="nofollow Lamont. The origin of this ring of mare ridges has long been controversial, but with this new data it appears that USGS mapper Dave Scott was correct, 36 years ago when he proposed it was a small impact basin covered by Tranquillitatis lavas. More surprising is the much stronger thinning anomaly centered west of " rel="nofollow Sinus Asperitatis. The existence of the West Asperitatis Basin explains the continuation of scattered high topography northwest of the curved rim of the Nectaris Basin. Like many other basins the WAB lacks a rim on one side - the east. Moving into Mare Fecunditatis is another surprising basin. This is surprising because although a basin is expected under each roughly circular patch of mare, this one, the Ibn Battuta-Lindbergh Basin, is smaller than expected. The contour lines don't seem to follow the mare ridges, suggesting a complicated story. Finally, at bottom right is a small anomaly that gives confidence in the others. The thinning is right in the middle of the previously hypothesized 500 km wide Balmer-Kapteyn Basin. As you explore the entire crustal thickness map the most unexpected thinning is for the Crüger Basin, which " rel="nofollow LPOD has already explored.
" rel="nofollow Chuck Wood
Related Links
Yoshiaki Ishihara and others (2009) " rel="nofollow Crustal thickness of the Moon: Implications for farside basin structures. Geophysical Research Letters 36, L19202, 4 PP., 2009. doi:10.1029/2009GL039708
COMMENTS?
Click on this icon File:PostIcon.jpg at the upper right to post a comment.



