Difference between revisions of "October 17, 2004"
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>Author & Editor:</b><br> | <p align="center" class="main_titles"><b>Author & Editor:</b><br> | ||
[mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Charles A. Wood]</p> | [mailto:tychocrater@yahoo.com Charles A. Wood]</p> | ||
| − | < | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> |
| − | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> | |
| − | < | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> |
| − | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> | |
| − | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> | |
| − | < | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> |
| − | < | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> |
| − | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> | |
| − | < | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> |
| − | + | <!-- Cleanup of credits --> | |
</td></tr> | </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:01, 15 March 2015
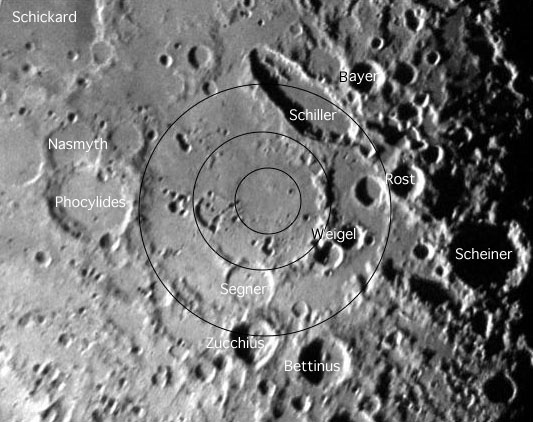
Rounding the Ellipses
Image Credit: Gary Seronik |
|
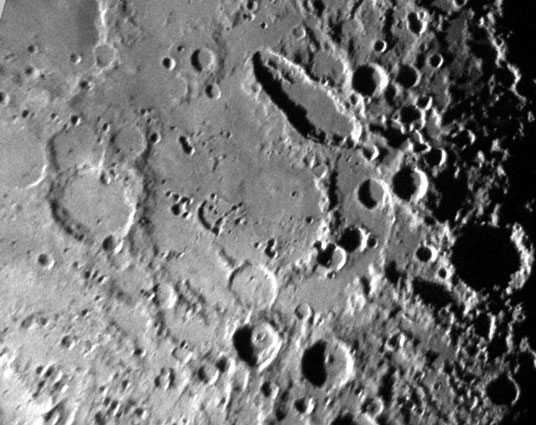
Rounding the Ellipses Because the Moon is a sphere, craters appear progressively more elliptical away from the center of the visible Moon toward the limb. The effect is most extreme right on the limb where we see craters in profile, but the foreshortening sometimes makes it difficult to understand the geometric shapes of craters anywhere within about 30 degrees of the limb. A prime example is the area shown in this image. You may not recognize it because the foreshortening has been removed. The image is centered on the Schiller-Zucchius multi-ring impact basin. The basin was not discovered until the 1960s when this area of the Moon was rectified by projecting a photo onto a globe and then re-photographing the globe from directly over the basin. As J-P Metsavainio demonstrated, now its easy to use Photoshop to digitally rectify images, and that is the technique used by Gary Seronik here. On the mouseover you can see the approximate positions and sizes of the three basin rings; the diameters are 335, 175 and 85 km. Most of the basin floor is covered by smooth material - probably mare basalts that have been lightened in hue by overlapping rays from younger craters. And notice that Schiller is still not circular in outline - it is a truly elliptical feature! Technical Details: Related Links: Yesterday's LPOD: Lunar Names Tomorrow's LPOD: 1826 Moon |
|
Author & Editor: |
COMMENTS?
Register, Log in, and join in the comments.